Next generation ultra-green energy.
Building the future of energy storage using the legacy of mining.
Future Mining’s energy storage system moves multiple heavy weights vertically in a legacy mine shaft to capture and release the potential gravitational energy of the weights. By simply using proven mechanical parts and disused mine shafts, Future Mining’s energy storage technology is cheap, long life and environmentally compelling.
Storing energy in this way uses no processed chemicals and has no performance degradation. Moving weights vertically allows for high Round Trip Efficiency and using legacy mine shafts allows reuse of existing structures, contributing to the circular economy and lowering costs.
Future Mining’s energy storage technology improves the economics of wind and solar power, leading to a faster and lower cost transition away from coal. Truly the next generation of ultra-green energy.
Using gravity to store energy
Future Mining’s gravity energy storage solution harnesses the fundamental principles of gravity and kinetic energy to store and dispatch energy by lifting and lowering heavy-weighted objects. Future Mining’s innovative technology was inspired by pumped hydro like Snowy Hydro 2.0.
Like pumped hydroelectricity, we use the gravitational potential energy of a mass moving between two heights. However, rather than water between two dams, Future Mining uses very dense materials to increase the energy. To overcome friction, a vertical height available from a mine shaft is used rather than an incline on the side of a hill.
How Future Mining energy storage works

Charge
Lift heavy weights to the top of the mine shaft using solar energy

Wait
Leave heavy weights stacked on the surface

Discharge
Lower heavy weights to the bottom of the mine shaft

Gravity
The gravity from the weight pulls a turbine, generating energy for the grid
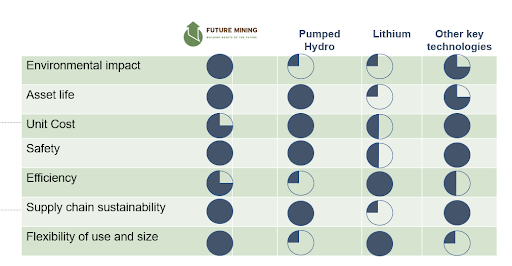
How it stacks up
Applications for the Future Mining energy storage technology
Our solution can provide services at all levels of the electricity system. We make renewable energy cheaper, make the grid more stable and reduce transmission costs, and can help mines and industrial plants reduce carbon emissions. We also have a role in supporting the local community energy schemes through firming distributed energy resources.

Power Generation
| Managing Intermittent renewable generation |
| Energy Arbitrage |
| Peak Shaving |
Transmission
| Ancillary Services |
| Transmission Constraints |
| Inertia Services |
| Responsive Flexibility Services |
| Voltage Support |

Distribution
| Reactive Power |
| Voltage Support |
| Local Security |
| Distribution Losses |

End Users
| Power Reliability |
| Energy Management |
| DER Firming |
| Mine Decarbonisation |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gravitational storage?
Gravitational storage refers to a process of converting electrical energy into gravitational potential energy through moving an object to a height. The energy is then released back to electrical energy at a later time by moving the object to a lower height, in the process turning an electric motor using the kinetic force of the descending object.
Where can Future Mining energy storage be deployed?
Future Mining’s system can be deployed in many types of mine shafts. With nearly 100,000 shafts in Australia, this offers many potential deployment locations. Locations with the best economic case include those with shafts built after 1950, with electrical infrastructure sill accessible, and with greater depth. Shafts over 300 metres deep offer very attractive energy economics.
What advantages does Future Mining have over chemical batteries?
Future Mining’s energy storage system is fundamentally more sustainable than chemical batteries. Some of the most important differentiating points include:
- Our parts can be locally sourced. Lithium batteries are produced using water intensive processing in South America, combined with remote chemicals in Africa, using industrial assembly in China.
- We use basic steel cables, motors and recycled and inert materials. Chemical batteries are future landfill liabilities and are hazardous materials.
- Gravitational energy systems do not leak energy over time, don’t degrade and have very long asset lives. The energy system needs long-term stable clean capacity. Future Mining can deliver equipment life 3 to 4 times longer than a chemical battery.
- Future Mining re-uses existing infrastructure. We take minesites, which are sitting idle today, and convert them into energy storage systems capable of accelerating the uptake of renewable energy.
Why is Future Mining storage technology simpler that other solutions?
Future Mining uses existing proven technology from the steel, mining and energy sectors to build the energy storage centre. We use cables, weighted blocks, mine winders, electric motors and off-the-shelf handling equipment to make our technology work. If you have case a fishing line, and dropped a rock down a hole before, then you can figure out how out technology works.
How much weight does a Future Mining energy storage centre move?
The weights moved depend on the depth and market configuration for an individual storage centre. For a large shaft, we move weights up to 40 metric tonnes, which give us the capability to store up to 10 kWh of energy per 100 metres of depth.
For context, an average car weighs 1.3 tonnes, meaning we drop objects weighing the equivalent of 30 cars.
How big are the mine shafts?
Mine shafts are generally very deep. Shallow shafts are 100-150 metres, while medium shafts are often 300 metres in depth. Modern shafts are concrete lined and can be more than 5 metres in diameter. Deep shafts can be over 1,000 metres in depth.
For some context, the Empire State Building is 380 metres, the Eiffel Tower 300 metres, Sydney Tower 305 metres, Petronas Towers 450 metres, and way out there, the Burj Khalifa 828 metres. Of course, nature wins with the Grand Canyon at 1,800 metres deep.
